Low E Glass
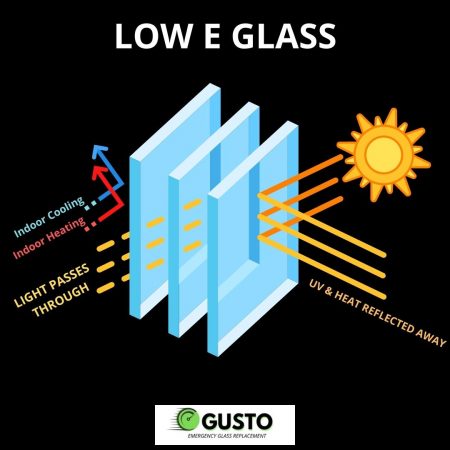

When it comes to windows, the type of glass you select is really important. According to experts, 70% of energy loss occurs in windows and doors, with 90% of window heat loss occuring through the glass. While energy efficiency is vital, the terminology used while studying different types of energy-efficient glass can be perplexing. We’ll go over what a Low-E glass is, why it’s energy efficient, the many types of Low-E coatings, and which is best for your location in this post.
What is Low E Glass?
Low E stands for ‘Low Emissivity,’ which refers to how much radiation is released or absorbed by a surface.
Low E glass is made with a very thin coating on one side that helps to reduce the amount of heat or cold that passes through the glass. It has a similar look to regular float glass, but it has better insulation properties. In recent years, Low E glass has become a popular way to insulate windows and increase energy efficiency in the home.
Uses for Low E Glass
Low E glass has become increasingly popular within the past decade as more homeowners have sought out energy efficient home renovations . It is now being used on windows, doors and skylights. Window manufacturers are also using Low-E coating on mirrors, shower walls and dividers between spaces. Making these updates in your home will help conserve energy throughout the year so that can save money on utilities , all while reducing your carbon footprint.
What is the main differences between soft vs hard low E coating?
The main differences between passive and solar control Low-E coatings are their emissive properties. Passive Low-E (hard coat) has a lower emissivity than Solar Control Low-E (soft coat).
Passive Low-E provides better thermal insulation, superior durability and offers benefits in energy conservation and environmental protection. It is used in the cold climates where the primary energy loss is through conduction, such as double pane windows or insulated glass units (IGUs).
Solar control low E coating – The Magnetron Sputtering Vapor Deposition (MSVD) technology is used to make low-E coatings, which implies the coating is applied off-line to pre-cut glass in a vacuum chamber at ambient temperature. This coating, often known as “soft-coat,” needs to be sealed so is usually only used in insulated glass units. The soft- coat has a reduced emissivity and provides better sun management. This coating provides the most effective sun management and performs well in warmer climates.
Low E Glass vs Double Glazing
Double glazing has been found to be more effective than low-E glass in areas where extremes of both heat and cold exist. While low-e glass is generally cheaper than double-glazing. Insulated glass units which combine double glazing or triple glazing with low E will offer the best performance when it comes to energy efficiency.
Click here to learn more about different types of glass
FAQ
Disadvantages of Low E Glass
The main disadvantage of low e glass is that it is expensive as compared to normal glass. Low e glass traps the heat radiating from objects and appliances inside the home, which may lead to overheating of interiors. The Low E coating can also be damaged by incorrect cleaning processes and contact with other metals.
Does Low E Glass Look Different
Low E glass looks similar to regular glass but the thin metallic oxide coating can sometimes be seen when the sun reflects off the glass, giving it a slightly green tint and wavy appearance when viewed at different angles.


Michael Peterson
Michael Peterson has been a glazier for over 20 years and is an expert in all things glass. He specialises in residential and commercial installations and repairs, including shower screens, mirrors and windows.
He's friendly and professional, with the experience to help you every step of the way and works in our Wentworth Point location providing glass repairs for our clients in the surrounding areas of Parramatta and Ryde.
